Allostery Model Help
Allostery Model Help
Developers:
Patrick Weinkam
Ben Webb
Acknowledgements:
Ursula Pieper
Elina Tjioe
Andrej Sali
Version main.1c3e6dc
AllosMod Help Pages
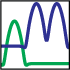
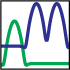
The AllosMod logo is comprised of two probability density functions that are used for the nonbonded distance
energy. The green probability density function translates to a single energy minima for interactions in the
allosteric site. The blue probability density function translates to a double energy minima for interactions in
the rest of the protein, i.e. the regulated region. Varying the radius of the allosteric site changes how the distance energy is distributed
across the structure, thereby driving the simulation to sample different regions of the conformational
space relevant to the allosteric transition.
For help page to model glycosylated proteins, click here.
For instructions on how to input a sequence into the first page, refer to the AllosMod-FoXS
help page
Running AllosMod locally
This web service is simply an interface to the base AllosMod protocol, which can be downloaded and run on any Linux machine or compute cluster.
The page below provides help to run batch jobs. Each input field in single landscape mode has a corresponding file/section below.
Single landscape runs will output the files described below corresponding to the options set by the user, i.e. the files from a single
landscape run can be uploaded as a batch run.
Server Input: Batch Mode
Email
A notification will be sent once the job is completed.
Name your model
Name your job so you can refer to it later.
Directories zip file
Upload a zip file containing a set of directories for each landscape that you want to model (no more than 100 such landscapes per job). To create such a file, put all the input files into one directory per landscape and type: zip -r input.zip dir1 dir2... For an example directory, click here. Please note that the directory name should not contain any spaces. Each directory should contain the following files:
PDB file(s): all structures used to create the energy landscape for the simulation.
Alignment file: (align.ali) contains one entry for each PDB file. Another entry (named pm.pdb) pertains to the sequence to be simulated.
This alignment file should be generated after an alignment procedure, as this alignment will be used to generate restraints for the simulation.
Multiple chains can be specified by using a "/" as a separator, the same specifications
used in MODELLER. There are many ways to create an alignment file including: 1) MODELLER
and 2) ClustalW. A suggested alignment file will be made if the uploaded alignment file
is faulty.
***WARNING*** Small errors in the alignment can cause big errors during a simulation due to energy conservation problems.
Make sure there are no misalignments in which adjacent residues are aligned far apart in sequence (alignment programs often do this at the beginning
or end of chains).
Structure list: (list) contains a list of all PDB files used to create the energy landscape for the simulation.
Refer to the LIGPDB and ASPDB options in input.dat to define interactions in the allosteric site.
Ligand File (optional): (lig.pdb) contains the structure of the ligand extracted from a ligand bound PDB file (defined
by LIGPDB in input.dat). A radius (rAS) around the ligand is used to define the allosteric site. If lig.pdb is excluded,
AllosMod will set up a landscape with as many energy minima as are described by structures in the list file.
Input file: (input.dat) contains one line per parameter as follows:
NRUNS = X
- is the number of independent simulations to run. (No more than 100, please.)
rAS = X (optional)
-
is the radius (in Ångstroms) around the coordinates of the ligand that will specify the allosteric site. If the file lig.pdb
is included, the allosteric site will be calculated using rAS and the coordinates in LIGPDB. Therefore, lig.pdb
must be extracted from LIGPDB.
SAMPLING = X (optional)
-
simulation -
- (Default) A simulation is set up for the user to run on his/her computer. Due to the large number of files
generated, AllosMod cannot currently run full simulations without overwhelming our other severs. For help running the
simulation, see section below called "To run the simulation."
moderate_am -
- Sampling is performed using a quick, unequilibrated simulation. This quick sampling will give a
representation of the types of conformations that are consistent with the modeled energy landscape. Set "SAMPLING = simulation"
to predict the relative populations of the conformations at equilibrium.
moderate_am_scan -
- As above, sampling is performed using a quick, unequilibrated simulation. In this case, simulations
should be performed at high temperature in order to access rarely populated structures. These rarely populated structures are
rapidly cooled using only restraints from adjacent residues, which does not change the global structure but allows helices to
form etc. Rarely populated structures are defined by their dissimilarity to the first structure in the list file
(SCAN_CUTOFF percent of trajectory snapshots are outputted).
delEmax = X (optional)
- is the maximum energy for each pairwise atomic distance contact, typically between 0.09 and 0.12 kcal/mol. If excluded,
the value will be assigned according to 3.6*(number of residues/number of distance interactions). See paper for more details.
LIGPDB = X (optional)
- is the PDB file used to define the allosteric site. AllosMod defines the allosteric site using the distance (rAS)
from the effector (lig.pdb) with respect to the LIGPDB coordinates.
ASPDB = X (optional)
- is the PDB file used to define the contacts in the allosteric site, i.e. the pairwise atomic distances
in ASPDB are used to determine the nonbonded distance energy. As an example, to run an effector unbound simulation:
1) include the effector bound and unbound PDB files in align.ali and list, 2) set ASPDB to the effector unbound PDB file, and
3) set LIGPDB to the effector bound PDB file.
DEVIATION = X (optional)
- is the distance (in Ångstroms) that the atoms will be randomized when creating the
initial structure (default is 1-10 Å depending on simulation type).
MDTEMP = X (optional)
- is the temperature (in degrees Kelvin) for the simulation (default is 300 K). Set MDTEMP to "scan" and the simulation
temperature will alternate between 300 K, 350 K, 400 K, 450 K, and 500 K. Therefore, directory 0 will have
a 300 K simulation, directory 1 will have a 350 K simulation, and so on until directory 5 that will restart the
sequence with a 300 K simulation.
SCAN_CUTOFF = X (optional)
- is the percent of trajectory snapshots outputted if sampling is moderate_am_scan. The default is 10 percent,
i.e. 0.1*NRUNS structures will be outputted selected by differing the most from the inputted PDB structure.
BREAK = True/False (optional)
- is an option to include chemical frustration (Weinkam et al. 2009 Biochemistry, p2394-2402). Chemical frustration
is modeled by breaking all interactions involving buried, charged residues. Regions with many buried, charged residues will
have high conformational variability.
SCLBREAK = X (optional)
- If BREAK=True, this number is used to scale the contacts with residues that cause chemical frustration.
ZCUTOFF = X (optional)
- If BREAK=True, this number is used to select which residues cause chemical frustration. ZCUTOFF is the z-score cut off
of the distribution involving the number of charged contacts per residue; residues with a z-score above this threshold
are predicted to cause chemical frustration.
LOCRIGID = True/False (optional)
- If set to True, secondary structure, corresponding to the input PDB files, will have increased stability
in the simulation. Increased stability is maintained by increasing the energy by a factor of 10 for all C alpha-C alpha
contacts between 2 and 5 residues apart.
COARSE = True/False (optional)
- is an option to coarse grain the energy landscape by restricting the nonbonded distance energy to include
C alpha and C beta atoms only. This allows very large proteins to be simulated without overwhelming the computer's memory. This
option is automatically set to True for proteins over 1500 residues.
{ADDITIONAL_RESTRAINT} {DISTANCE} {STANDARD_DEVIATION} {INDICES} (optional)
- is used to add additional restraints between residues.
ADDITIONAL_RESTRAINT can be HARM, LOBD, or UPBD corresponding to a distance restraints that are harmonic, lower bounded only,
or upper bounded only, respectively. DISTANCE and STANDARD_DEVIATION corresponds to the distance (in Ångstroms)
between two atoms in the residues specified in INDICES. If residue index is an amino acid, atom type will be CA, otherwise atom type will
be the first present: N, P, C, or O. INDICES is a list of residue indices separated by commas.
Restraints are added between each successive pair of indices, i.e. between i1 and i2, between i3 and i4, ...
The residue index corresponds to the position in the input alignment file. Therefore, if there are multiple chains, the index for the
first residue in the second chain will be one more than the index for the last residue in the first chain
(refer to any output PDB for simplicity).
(for example, click here)
Alter residue contact energies (optional): break.dat contains a list of residues whose pairwise contact energies (delEmax) will be scaled by a specifed value. Each line contains one residue index (corresponding to simulated sequence) in the first column and one scaling factor in the second column. For example, to reduce all contact energies for residue 30 by 90 %, break.dat would have one line with "30 0.1". break.dat is created automatically by setting BREAK=True, however, the user may specify any desired residues and scaling factors by including break.dat in a batch run.
Server Output
The output is a zip file containing the same directories that were uploaded and subdirectories for each simulation. Each subdirectory will contain a MODELLER script (model_run.py), a unique starting structure (random.ini), a restraint file containing interactions that will define the energy landscape (converted.rsr), log files, and other output files. If you opted to run short, unequilibrated simulations via the server then each subdirectory will contain pdb files named pm.pdb.B1*. If you opted to set up a longer simulation to be run locally, then see the following section.
***To run the simulation
To run, navigate to a run directory. Each run directory contains a unique starting structure (random.ini) and a unique run script (model_run.py), then type: "$MODELLER_HOME/bin/mod${MODELLER_VERSION} model_run.py". The script will output 2000 snapshots by default (pm.pdb.B10010001.pdb to pm.pdb.B30000001.pdb) as well other data files. AllosMod implements the Automodel class used in MODELLER for comparative modeling, however the optimization and refinement steps have been modified to allow for constant temperature molecular dynamics simulations. For each run directory, there is a file allosmod.py. This file contains the method consttemp that controls the simulation schedule and temperature (MDtemp). For help with script details, refer to the MODELLER help pages.
To analyze the simulation
Download a zip file containing example directories and analysis scripts to run on any linux/unix based machine (click here). The allosmod_analysis.sh script will check the simulations for possible errors as well as output several files including: 1) energies 2) Boltzmann weighted probabilities 3) local structural similarity metrics Qi. See README file for a full description.