|
 |
About Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
SAXS experiment determines 1-dimensional structural information, termed SAXS profile, which is the scattering intensity of a molecule as a function of spatial frequency. The profile can be converted into a radial distribution function of the molecule with Fourier transform. The experiment is performed on a purified protein sample in solution, resulting in a data that is a rotational and conformational average (1 to 3 nm resolution). There are practically no limitations on molecules sizes [5-10].
There are two major approaches to structure prediction using the scattering profile: (i) ab initio methods vs. (ii) rigid body modeling. If the structure of the assembly or its individual subunits is not available, only ab initio methods can be used. If the structure of the assembly or its components is known, rigid body modeling methods can be applied. In rigid body modeling, atomic resolution models for the studied assembly are generated by docking methods, and the theoretical scattering profile of the models is compared to the experimental one.
FoXS
FoXS is a method for computing a theoretical scattering profile of a structure and fitting of experimental profile [1-3]. FoXS can be used as a basic tool for numerous structural modeling applications with SAXS data:
- Comparison of solution and X-ray structure conformations
- Modeling of different conformation, i.e. model active conformation starting from non-active
- Structural characterization of flexible proteins
- Assembly of multi domain proteins starting from single domain structures
- Assembly of multi protein complexes
- Fold recognition and comparative modeling
- Determination of biologically relevant state from the crystals
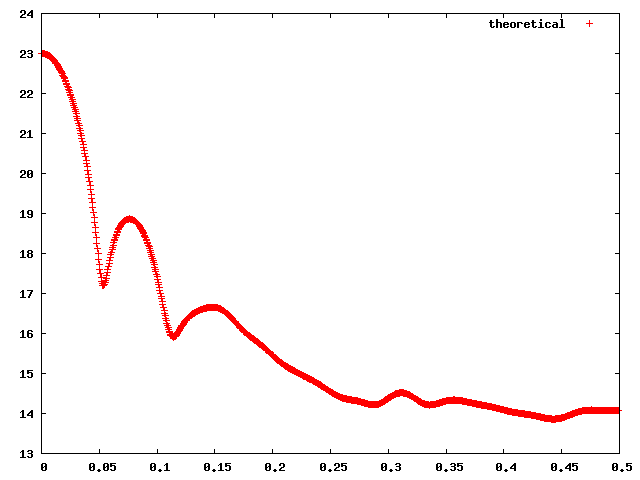
The input to the webserver is a PDB or mmCIF format file and experimental SAXS profile (if available). FoXS computes the theoretical profile and outputs it as a text file and as a plot of intensity (log scale) vs. q. The profile is computed using Debye formula for spherical scatterers [5].
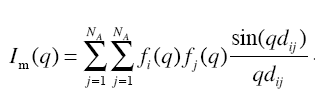
where fi(q) and fj(q) represent the isotropic atomic form factors of the atoms i and j, and dij is the Euclidean distance between these atoms.
If experimental SAXS profile is available, FoXS will fit the theoretical profile to the experimental one. The quality of the fit is measured by χ function.
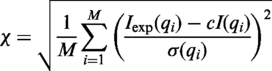
where c is a scaling parameter and σ is the experimental error.
MultiFoXS
If multiple PDB/mmCIF files were uploaded by the user, in addition to profile calculation for each structure, the server will also run enumeration and fitting of multiple structures to the input profile [1, 4]. See MultiFoXS example for details.
The method is useful in cases of flexible multi-domain proteins or mixtures (for example proteins that exist as a mixture of monomers and dimers in solution). If you need to sample the conformational space of your protein, try MultiFoXS webserver.
References
- D. Schneidman-Duhovny, M. Hammel, JA. Tainer, and A. Sali. Accurate SAXS profile computation and its assessment by contrast variation experiments. Biophysical Journal 2013.
- D. Schneidman-Duhovny, M. Hammel, and A. Sali. FoXS: A Web server for Rapid Computation and Fitting of SAXS Profiles. NAR 2010.38 Suppl:W540-4 [ FREE Full Text ].
- Schneidman-Duhovny D, Hammel M, Tainer JA, and Sali A. FoXS, FoXSDock and MultiFoXS: Single-state and multi-state structural modeling of proteins and their complexes based on SAXS profiles NAR 2016 [ FREE Full Text ].
- Pelikan M, Hura GL, Hammel M. Structure and Flexibility within proteins as identified through small angle X-ray scattering. General Physiology and Biophysics. 2009;28:174 - 89.
- Debye, P. 1915. Zerstreuung von röntgenstrahlen. Scattering from non-crystalline substances, Ann. Phys. 46:809-823.
- Biological Small Angle X-ray Scattering Wiki entry.
- M. H. Koch, P. Vachette, and D. I. Svergun. Small-angle scattering: a view on the properties, structures and structural changes of biological macromolecules in solution. Q Rev Biophys 36 (2), 147 (2003).
- M. V. Petoukhov and D. I. Svergun. Analysis of X-ray and neutron scattering from biomacromolecular solutions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 17 (5), 562 (2007).
- C. D. Putnam, M. Hammel, G. L. Hura et al., X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) combined with crystallography and computation: defining accurate macromolecular structures, conformations and assemblies in solution. Q Rev Biophys 40 (3), 191 (2007).
- G. L. Hura, A. L. Menon, M. Hammel et al., Robust, high-throughput solution structural analyses by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Nat Methods 6 (8), 606 (2009).
- F. Forster, B. Webb, K. A. Krukenberg et al., Integration of small-angle X-ray scattering data into structural modeling of proteins and their assemblies. J Mol Biol 382 (4), 1089 (2008).
If you use FoXS, please cite:
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Hammel M, Tainer JA, and Sali A. Accurate SAXS profile computation and its assessment by contrast variation experiments. Biophysical Journal 2013. 105 (4), 962-974
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Hammel M, Tainer JA, and Sali A. FoXS, FoXSDock and MultiFoXS: Single-state and multi-state structural modeling of proteins and their complexes based on SAXS profiles NAR 2016 [ FREE Full Text ]
Contact:
